Frequently Asked Questions
Please reach us at support@curaveil.com if you cannot find an answer to your question.
Q: What is UVC Radiation?
A: UVC radiation is the highest energy portion of the UV radiation spectrum.
UVC radiation from the sun does not reach the earth’s surface because it is blocked by the ozone layer in the atmosphere. Thus, the only way that humans can be exposed to UVC radiation is from an artificial source like a lamp or laser.
Q: What are the risks of exposure to UVC radiation?
A: UVC radiation can cause severe burns of the skin and eye injuries (photokeratitis). Avoid direct skin exposure to UVC radiation and never look directly into a UVC light source, even briefly. Skin burns and eye injuries from UVC exposure usually resolve within a week with no known long-term damage. Since the penetration depth of UVC radiation is very low, the risk of skin cancer, cataracts or permanent vision loss is also thought to be very low. The type of eye injury associated with exposure to UVC causes severe pain and a feeling of having sand in the eyes. Sometimes people are unable to use their eyes for one to two days. It can occur after a very short exposure (seconds to minutes) to UVC radiation.
If you have experienced an injury associated with using a UVC lamp, we encourage you to report it to the FDA.
Q: What are the risks associated with using some UVC lamps?
A: Some UVC lamps emit small amounts of UVB radiation. Therefore, exposure to a high dose or prolonged low dose of radiation from some UVC lamps can potentially contribute to effects like cataracts or skin cancer that are caused by cumulative exposure to UVB radiation.
Additionally, some UVC lamps generate ozone which could cause irritation to breathing passages (that is nose, throat, and lungs), particularly for those who have respiratory sensitivity such as asthma or allergies. Exposure to high levels of ozone gas may also worsen chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma, or increase vulnerability to respiratory infection.
Q: What effect does UV radiation have on my body?
Both UVA and UVB rays can cause damage to your skin. Sunburn is a sign of short-term overexposure, while premature aging and skin cancer are side effects of prolonged UV exposure.
Certain oral and topical medicines, such as antibiotics, birth control pills, and benzoyl peroxide products, as well as some cosmetics, may increase skin and eye sensitivity to UV in all skin types. Check the label and ask your doctor for more information.
Q: What are the different types of UV radiation?
The most common form of UV radiation is sunlight, which produces three main types of UV rays:
- UVA
- UVB
- UVC
UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths. While UVA and UVB rays are transmitted through the atmosphere, all UVC and some UVB rays are absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer. So, most of the UV rays you come in contact with are UVA with a small amount of UVB.
Like all forms of light on the EM spectrum, UV radiation is classified by wavelength. Wavelength describes the distance between the peaks in a series of waves.
- UVB rays have a short wavelength that reaches the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis)
- UVA rays have a longer wavelength that can penetrate the middle layer of your skin (the dermis)
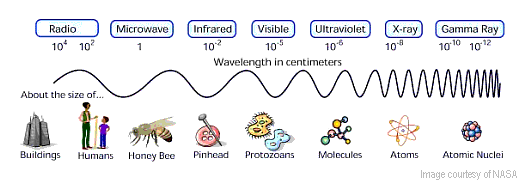
Q: How is radiation classified on the electromagnetic spectrum?
Electromagnetic radiation is all around us, though we can only see some of it. All EM radiation (also called EM energy) is made up of minute packets of energy or 'particles,' called photons, which travel in a wave-like pattern and move at the speed of light. The EM spectrum is divided into categories defined by a range of numbers. These ranges describe the activity level, or how energetic the photons are, and the size of the wavelength in each category.
For example, at the bottom of the spectrum radio waves have photons with low energies, so their wavelengths are long with peaks that are far apart. The photons of microwaves have higher energies, followed by infrared waves, UV rays, and X-rays. At the top of the spectrum, gamma rays have photons with very high energies and short wavelengths with peaks that are close together.
Q: What is UV Radiation?
All radiation is a form of energy, most of which is invisible to the human eye. UV radiation is only one form of radiation and it is measured on a scientific scale called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum.
UV radiation is only one type of EM energy you may be familiar with. Radio waves that transmit sound from a radio station’s tower to your stereo, or between cell phones; microwaves, like those that heat your food in a microwave oven; visible light that is emitted from the lights in your home; and X-rays like those used in hospital X-ray machines to capture images of the bones inside your body, are all forms of EM energy.
UV radiation is the portion of the EM spectrum between X-rays and visible light.
Copyright © 2023-2024 Curaveil© - All Rights Reserved.
Powered by Health Web Systems Canada